 |
Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2015
Making development sustainable: The future of disaster risk management |
 |
Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2015
Making development sustainable: The future of disaster risk management |
|
|
130
Part II - Chapter 6
Notes
1 http://iog.ca/defining-governance.
2 For more information on local, national and regional HFA reports, see https://www.preventionweb.net/english/hyogo/ progress/?pid:73&pil:1. 3 www.duryognivaran.org. 4 https://www.unisdr.org/campaign/resilientcities. 5 Various sources: http://www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/11/2321/2011/ nhess-11-2321-2011.pdf; http://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-30453552; http://www.lemonde.fr/planete/article/2014/12/12/xynthia-lancien-maire-de-la-faute-sur-mer-condamne-a-quatre-ans-deprison-ferme_4539436_3244.html (accessed 11 January 2015). 6 For more information on the Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility, see http://www.ccrif.org/content/about-us and the Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment and Financing Initiative: http://pcrafi.sopac.org/ (accessed 28 August 2014). 7 For more information on these initiatives, see www. theriseinitiative.org and http://www.un.org/climatechange/ summit/action-areas. and environmental responsibility are increasingly being adopted by businesses to enhance their value proposition (
 UNECE, 2014 UNECE, 2014 UNECE (United Nations Economic Commission for Europe). 2014,Standards and Normative Mechanisms for Disaster Risk Management, Background Paper prepared for the 2015 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction. Geneva, Switzerland: UNISDR.. UNECE (United Nations Economic Commission for Europe). 2014,Standards and Normative Mechanisms for Disaster Risk Management, Background Paper prepared for the 2015 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction. Geneva, Switzerland: UNISDR.. Click here to view this GAR paper. The way in which disaster risk management has been approached is now being challenged by these innovative efforts, most of which are currently in a phase of exploration rather than consolidation. As the HFA comes to a close, therefore, disaster risk management finds itself at something of a crossroads. Disasters such as Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines in 2013 are blowing away the veils of hyper-reality to show that even countries with apparently mature and comprehensive disaster risk governance arrangements in place are challenged by continued risk accumulation. The governance approach based on the disaster management cycle and represented by a specialized disaster risk management sector may have reached its limit, while at the same time a new governance paradigm has yet to emerge.
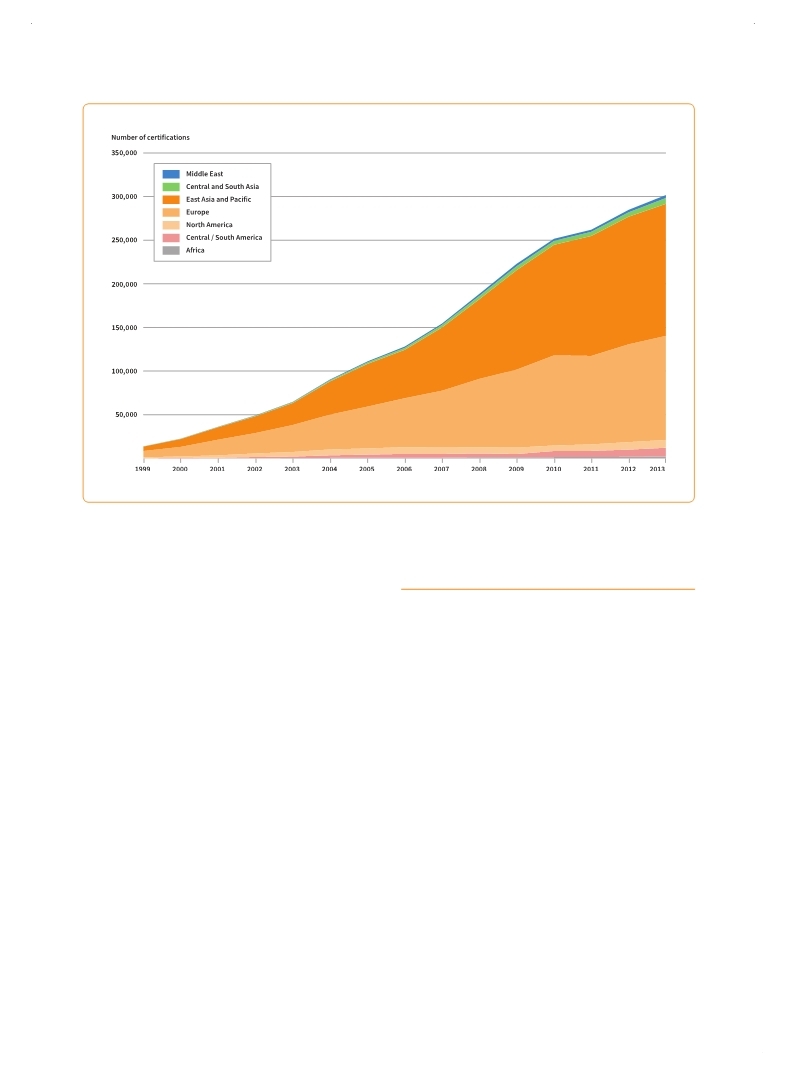
(Source: ISO, 2014.)
Figure 6.5 Uptake of environmental management system standards
|
 
Page 1Page 10Page 20Page 30Page 40Page 50Page 60Page 70Page 80Page 90Page 100Page 110Page 120Page 121Page 122Page 123Page 124Page 125Page 126Page 127Page 128Page 129Page 130Page 131->Page 132Page 133Page 134Page 135Page 136Page 137Page 138Page 139Page 140Page 141Page 142Page 143Page 144Page 150Page 160Page 170Page 180Page 190Page 200Page 210Page 220Page 230Page 240Page 250Page 260Page 270Page 280Page 290Page 300Page 310
|
|
 
|
 
|
