Paving farm roads with rapid hardening concrete composite mat

Korean engineers develop an easy-to-install, economical, and quick-to-use concrete mat as an alternative to traditional road paving.
Introduction
A conducive road network is integral to the economic growth of a country. Better roads mean efficient movement of people and goods, as well as improved access to health, education, and economic facilities and services. This is why most countries allocate substantial investments for infrastructure that improves connectivity, mobility, and trade routes.
Often, resources are primarily allocated for the development or maintenance of major highways and roads that connect cities or towns due to their greater economic, geographic, and political significance. While governments often have plans and programs in place, rural and farm roads may receive less attention when it comes to maintenance and upgrades due to several factors such as limited resources or competing priorities.
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT), a government-funded research institute in the Republic of Korea, has developed a rapid hardening concrete composite mat technology which offers countries a high-performance, low-cost, and time-efficient option for paving and repairing roads networks for improved connectivity specially for rural and farm roads.
What road improvement technology was developed by KICT?
Traditional road paving involves the use of asphalt or concrete mixtures. The process usually consists of six steps: 1) grading and scoping to establish the desired road contour, 2) preparation and compaction to stabilize the base, 3) proof rolling, undercutting, and base repair to address irregularities, 4) application of the binder to enhance adhesion and structural integrity, 5) installation of the asphalt surface, and lastly 6) final compaction and smoothing of the asphalt to achieve durability.
In addition to these steps, asphalt paving requires the use of heavy equipment, such as motor graders, asphalt pavers, compactors, excavators, and wheel loaders. Asphalt-paved roads can be opened to traffic within 12 to 24 hours after the paving is complete.
Meanwhile, KICT has developed a rapid hardening concrete composite mat pavement technology, a solution consisting of a non-woven fabric enclosing rapid hardening mortar and a woven fabric. The mat is prefabricated in a factory. The site installation process is simplified to just four steps: 1) preparing and compacting the subbase to establish a sturdy foundation, 2) laying the composite mat, 3) securing the mat with durable pins, and 4) spraying water on it to activate the rapid hardening properties and initiate the curing process.
Unlike traditional asphalt paving, this process does not require multiple pieces of heavy equipment. Instead, it can be quickly installed with material-moving equipment such as an excavator. After installation, the road can be opened to traffic within 4 to 6 hours.
Components of Rapid Hardening Concrete Composite Mat

Source: KICT.
What makes this technology suitable for Southeast Asia?
KICT's technology offers a convenient alternative to addressing unpaved and farm roads. These roads often become impassable due to ground loss, subsidence, and mud formation, especially during the rainy season.
The concrete composite mats stop rainwater from infiltrating the unpaved road surface. This preserves the road’s bearing capacity and helps prevent soil erosion.
The ease of construction and reduced dependence on heavy equipment can also result in cost savings.
The quick installation process and fast curing time of the composite mats allow for rapid deployment. This minimizes the disruption to transportation networks and communities during construction.
These composite mats can also be applied to various geotechnical structures such as slopes, embankments, and channels.
Advantages of Rapid Hardening Concrete Composite Mat
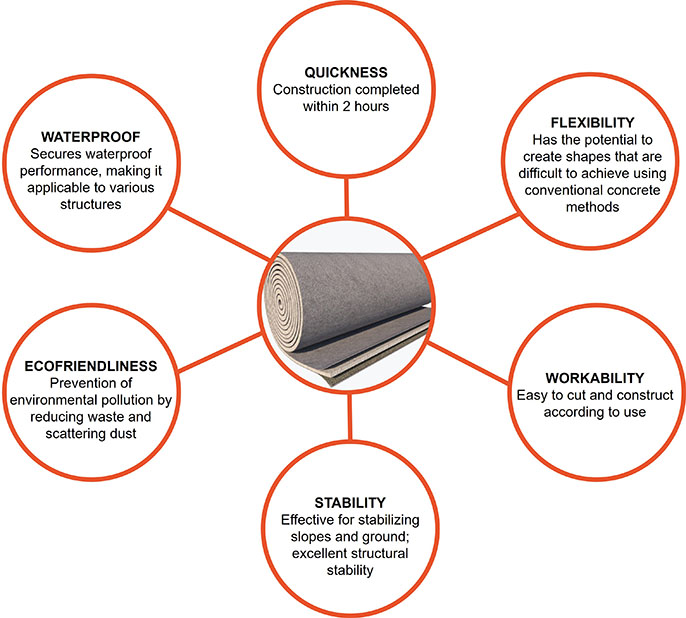 Source: KICT.
Source: KICT.
How was this technology tested?
Following industry standards, an authorized certification laboratory in the Republic of Korea has tested the performance and applicability of this solution in various construction projects. Field tests were also conducted at multiple domestic sites. The results demonstrate that this technology meets constructability and quality metrics when applied to unpaved roads. The tests also show that this technology cures faster and possesses greater strength than traditional concrete. Additionally, the mat can bend and adapt better to surface contours without cracking or breaking.
Installing Rapid Hardening Concrete Composite Mat on Slopes

Source: KICT.