 |
Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2013
From Shared Risk to Shared Value: the Business Case for Disaster Risk Reduction |
 |
Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2013
From Shared Risk to Shared Value: the Business Case for Disaster Risk Reduction |
|
|


|
The Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction: a retrospective
This 2013 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction, From Shared Risk to Shared Value: The Business Case for Disaster Risk Reduction (GAR13), is the third biennial report coordinated by the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduc- tion (UNISDR).
The first Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction, Risk and Poverty in a Changing Cli- mate (GAR09), as well as the second, Revealing Risk – Redefining Development (GAR11), focused primar- ily on public policy and the role of national and local governments in disaster risk reduction. The key mes- sage of GAR09 was that addressing the underlying
risk drivers is critical not only to the achievement of the Hyogo Framework of Action (HFA)i , but also the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and climate change adaptation. GAR11 built on that evidence to provide guidance to governments on how to effectively manage their disaster risk.
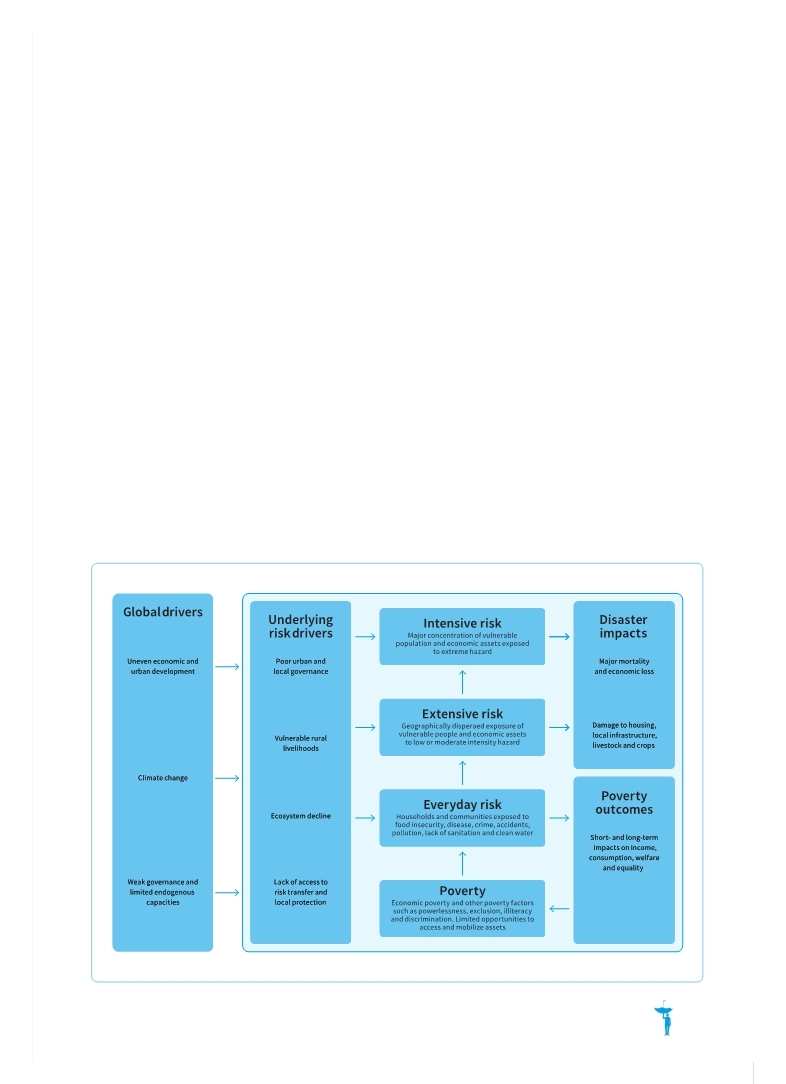
GAR09 highlighted how intensive disaster risk is disproportionally concentrated in lower-income countries with weak governance. Within countries, it showed how underlying drivers—such as poor urban governance, vulnerable rural livelihoods and declining ecosystems—concentrate extensive di- saster risk in low-income communities and house- holds and drive further the depth and breadth of poverty, undermining development (Figure 0.1).
xiii
Preface
(Source: UNISDR, 2009
UNISDR. 2009.,Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction: Risk and poverty in a changing climate., United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction., Geneva,Switzerland: UNISDR.. . |



 |
