 |
Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2013
From Shared Risk to Shared Value: the Business Case for Disaster Risk Reduction |
 |
Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2013
From Shared Risk to Shared Value: the Business Case for Disaster Risk Reduction |
|
|


|
It also found that, although progress was being made to strengthen capacities for disaster pre- paredness and response, governments were chal- lenged to tackle underlying risk drivers.
GAR11 provided further evidence on why disaster risk was increasing and why existing efforts in its reduction were failing to address underlying risk driv- ers. The report provided an updated analysis of global disaster risk and loss trends and a second biennial review of progress against the HFA. It then identified political and economic imperatives for increased public investment in disaster risk reduction. A cost-effective strategy for layering disaster risk management was proposed—which layers of risks to reduce; which to insure; and which to retain.
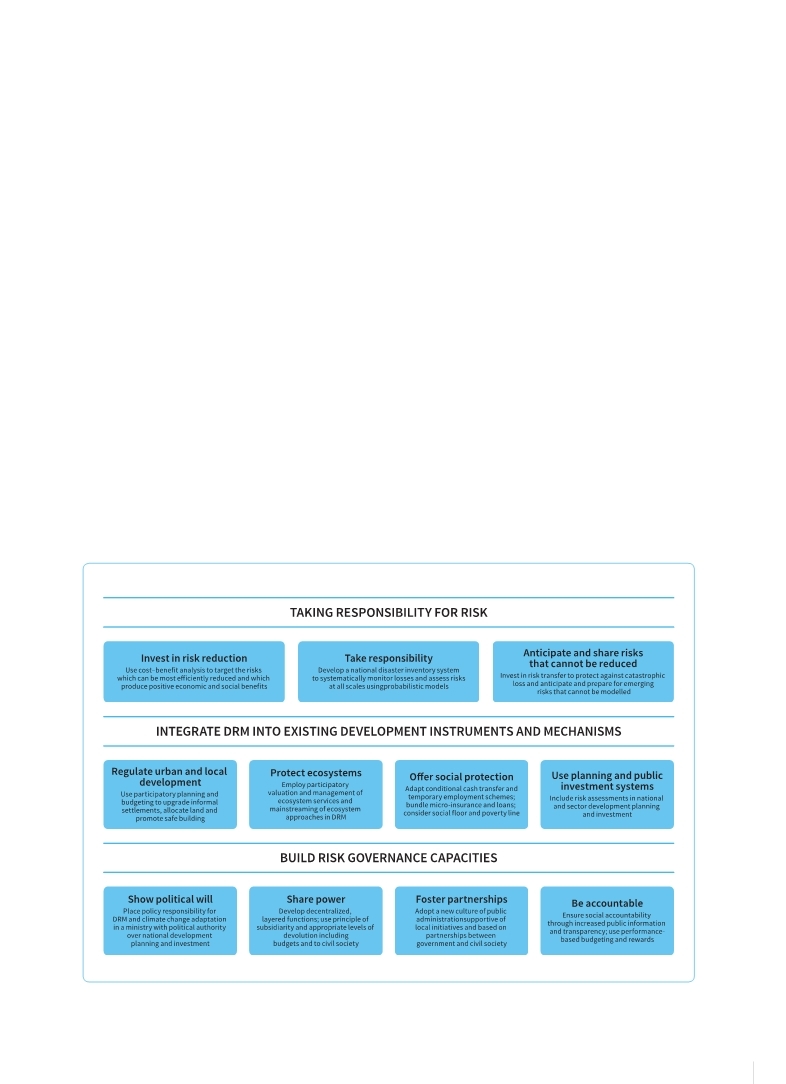
GAR11 described the mechanisms through which governments can deliver responsible and consis- tent policies for risk reduction, integrate disaster risk management into existing development
instruments, and build and strengthen risk gover- nance capacities (Figure 0.2).
In most economies, public investment represents only 15–30 percent of gross fixed capital formation. ii How the other 70–85 percent of investment is made, therefore, has far-reaching consequences on disaster risk accumulation and on the underlying risk drivers identified in GAR09. In future, trillions of dollars of new business investment will pour into hazard-exposed regions, largely determining the future of disaster risk.
Despite their importance, business investment practices were neither highlighted in the HFA nor have interactions between business investment and disaster risk and the factors that mediate those interactions been seriously examined. Like the HFA, research and literature on this topic has concentrat- ed on the role of governments, communities and households rather than of businesses.
xiv
Preface
Figure 0.2 GAR11- Key elements for successful disaster risk management (DRM) across governance scales and development sectors
(Source: UNISDR, 2011
UNISDR. 2011.,Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction: Revealing Risk, Redefining Development., United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction., Geneva,Switzerland: UNISDR.. . |



 |
